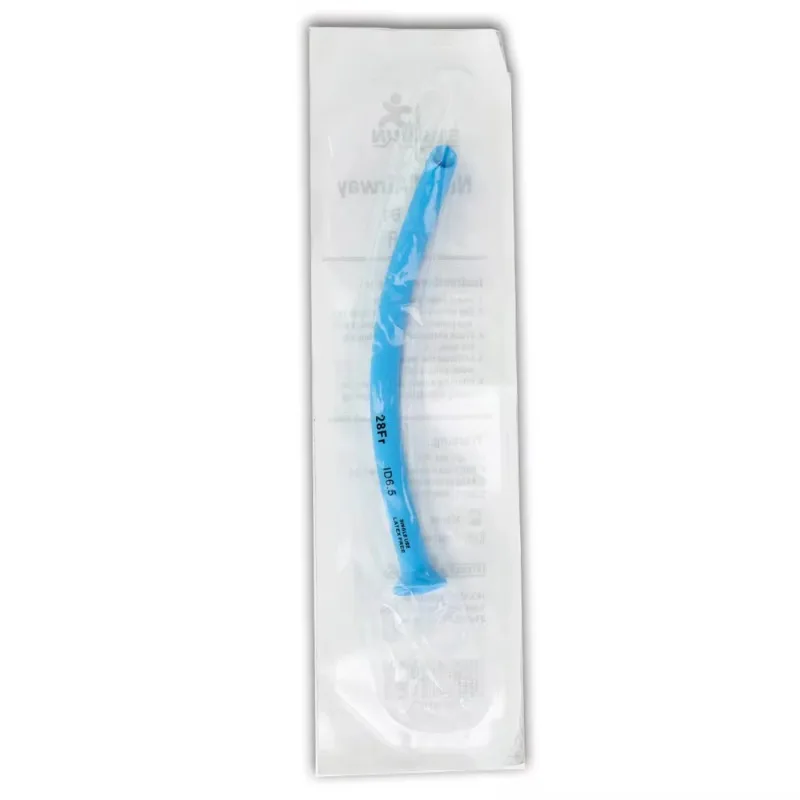
Skip to product information

$7.00 USD
#detail_decorate_root .magic-0{border-bottom-style:solid;border-bottom-color:#53647a;font-family:Roboto;font-size:24px;color:#53647a;font-style:normal;border-bottom-width:2px;padding-top:8px;padding-bottom:4px}#detail_decorate_root .magic-1{vertical-align:top}#detail_decorate_root .magic-2{vertical-align:top;display:block;padding-right:4px;box-sizing:border-box;padding-left:4px}#detail_decorate_root .magic-3{vertical-align:top;padding-bottom:4px;box-sizing:border-box;padding-top:4px}#detail_decorate_root .magic-4{padding:0;margin:0;white-space:pre-wrap;font-size:14px}#detail_decorate_root .magic-5{font-size:16px}#detail_decorate_root .magic-6{margin-bottom:10px;line-height:0}#detail_decorate_root .magic-7{margin-bottom:0}#detail_decorate_root .magic-8{position:relative;width:100%}#detail_decorate_root .magic-9{width:750px}#detail_decorate_root .magic-10{overflow:hidden;width:750px;height:2390.25px;margin-top:0;margin-bottom:0;margin-left:0;margin-right:0}#detail_decorate_root .magic-11{margin-top:0;margin-left:0;width:750px;height:2390.25px}#detail_decorate_root .magic-12{font-size:18px}